CAICCAIC: Centre for Artificial Intelligence Challenge on Conversational AI Correctness
=======================================================================================
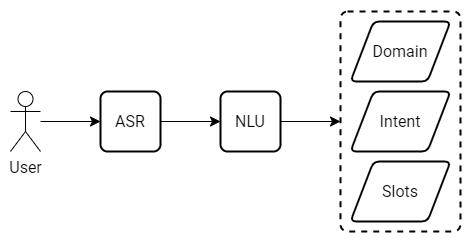
Develop Natural Language Understanding models that are robust to speech recognition errors.
# Task Description
## Introduction
Regardless of the near-human accuracy of Automatic Speech Recognition in general-purpose transcription tasks, speech recognition errors can significantly deteriorate the performance of a Natural Language Understanding model that follows the speech-to-text module in a virtual assistant. The problem is even more apparent when an ASR system from an external vendor is used as an integral part of a conversational system without any further adaptation.
The goal of this competition is to develop Natural Language Understanding models that are robust to speech recognition errors.
The approach used to prepare data for the challenge is meant to promote models robust to various types of errors in the input, making it impossible to solve the task by simply learning a shallow mapping from incorrectly recognized words to the correct ones. This reflects real-world scenarios where the NLU system is presented with inputs that exhibit various disturbances due to changes in the ASR model, acoustic conditions, speaker variation, and other causes.
 ## Dates
- Feb 13, 2023: Training data available (English)
- Feb 20, 2023: Training data available (other languages)
- May 17, 2023: Test data available
- May 31, 2023: Deadline for submitting the results
- June 04, 2023: Announcement of the final results, sending invitations for submitting papers
- July 04, 2023: Deadline for submitting invited papers
- July 11, 2023: Author notification
- July 31, 2023: Final paper submission, registration
- Sept 20, 2023: Challenges in Natural Language Processing Symposium
## Data
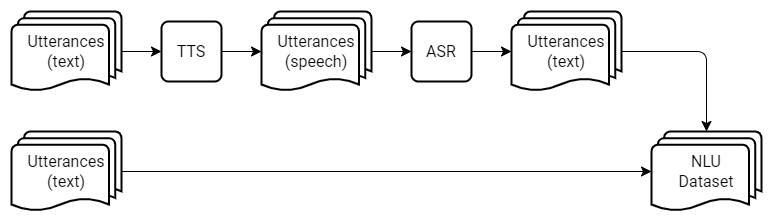
The training set is derived from [Leyzer: A Dataset for Multilingual Assistants](https://github.com/cartesinus/leyzer). It consists of user utterances along with the semantic representation of the commands targeted at a virtual assistant. A fraction of the utterances in the training set is contaminated with speech recognition errors; however, to make the task more challenging, we left the majority of the utterances intact. The erroneous samples were obtained from user utterances using a TTS model followed by an ASR system.
## Dates
- Feb 13, 2023: Training data available (English)
- Feb 20, 2023: Training data available (other languages)
- May 17, 2023: Test data available
- May 31, 2023: Deadline for submitting the results
- June 04, 2023: Announcement of the final results, sending invitations for submitting papers
- July 04, 2023: Deadline for submitting invited papers
- July 11, 2023: Author notification
- July 31, 2023: Final paper submission, registration
- Sept 20, 2023: Challenges in Natural Language Processing Symposium
## Data
The training set is derived from [Leyzer: A Dataset for Multilingual Assistants](https://github.com/cartesinus/leyzer). It consists of user utterances along with the semantic representation of the commands targeted at a virtual assistant. A fraction of the utterances in the training set is contaminated with speech recognition errors; however, to make the task more challenging, we left the majority of the utterances intact. The erroneous samples were obtained from user utterances using a TTS model followed by an ASR system.
 The training data are located in the `train` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The `train` directory contains two files:
- **in.tsv** with four columns:
a. sample identifier: `306`,
b. language code: `en-US`,
c. data split type: `train`,
d. utterance: `adjust the temperature to 82 degrees fahrenheit on my reception room thermostat`.
- **expected.tsv** with three columns representing:
a. domain label: `Airconditioner`,
b. intent label: `SetTemperatureToValueOnDevice`,
c. annotations for slot values: `{'device_name': 'reception room', 'value': '82 degrees fahrenheit'}`.
For experimentation, we provide the validation dataset located in the `dev-A` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. It was created using the same pipeline as the `train` dataset.
For the sake of preliminary comparison of results between contestants and self-evaluation we provide test dataset located in `test-A` directory of `cnlps-caiccaic` repository.
It contains only input values, while expected values hidden for contestants and are used by gonito platform to evaluate submissions.
The test set prepared for the final evaluation will be released on May 17, 2023, and placed in the `test-B` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The goal of the task is to develop NLU models that are robust to speech recognition errors regardless of their type and origin, therefore participants **should not** assume that the same TTS and ASR models will be used for the preparation of the test data as for the preparation of the training data. Also, the ratio of utterances containing speech recognition errors to intact utterances will vary, with far more erroneous samples found in the test set.
| | Train | Test |
|------------|-------------|------------|
|Sentences | 14524 | 3633 |
|Avg length | 9.35 | 9.28 |
|Min length | 1 | 1 |
|Max length | 33 | 30 |
|Domains | 21 | 21 |
|Intents | 193 | 193 |
|Slots types | 80 | 79 |
## Submissions
- The solutions for the task are to be submitted via the Gonito platform challenge available at .
- For `in.tsv` file located in `test-A` (or `test-B`) directory, the participants are expected to provide `out.tsv` file in the same directory.
- Each row of `out.tsv` should contain the predictions for the corresponding row in `in.tsv`.
- The format of `out.tsv` file is the same as the format of `train/expected.tsv`.
## Rules
1. Participants are allowed to use any publicly available data.
2. Participants are allowed to use any publicly available pre-trained models.
3. Manual labeling is forbidden.
4. Max. 5 submissions per day are allowed.
5. Teams may consist of one or more people. There is no restriction on the size of the team. Only one team representative should submit the team's solution to the platform.
6. If it turns out that the solutions submitted by two different teams have the same score, the team that submitted the solution earlier would be ranked higher.
7. To be included in the final ranking, a team should provide a report describing their solution.
8. The report should conform to the requirements specified in the exemplary document provided at .
9. The best scoring submission on `test-B` for which a report is provided wins.
## Special session at FedCSIS 2023:
The authors of selected submissions will be invited to prepare the extended versions of their reports for publication in the conference proceedings and presentation at FedCSIS 2023. The Organizing Committee will make the selection based on the final evaluation results, the quality of submitted reports, and the originality of the presented methods.
## Evaluation
To create the final ranking, the submissions will be scored using **Exact Match Accuracy** (EMA), i.e.
> the percentage of utterance-level predictions in which domain, intent, and all the slots are correct.
Besides EMA scores, we will also report the following auxiliary metrics:
1. Domain accuracy:
> the percentage of utterances with correct domain prediction.
2. Intent accuracy:
> the percentage of utterances with the correct intent prediction.
3. Slot Word Recognition Rate:
> Word Recognition Rate calculated on slot annotations which is the percentage of correctly annotated slot values.
## Organizing Committee
- Marek Kubis, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poland
- Paweł Skórzewski, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poland
- Marcin Sowański, Samsung Research Poland
- Tomasz Ziętkiewicz, Samsung Research Poland
We set up a “CNLPS” Discord server to discuss the CAICCAIC challenge. Please join it to ask any task-related questions: https://discord.gg/VvjHhh7rbF
The training data are located in the `train` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The `train` directory contains two files:
- **in.tsv** with four columns:
a. sample identifier: `306`,
b. language code: `en-US`,
c. data split type: `train`,
d. utterance: `adjust the temperature to 82 degrees fahrenheit on my reception room thermostat`.
- **expected.tsv** with three columns representing:
a. domain label: `Airconditioner`,
b. intent label: `SetTemperatureToValueOnDevice`,
c. annotations for slot values: `{'device_name': 'reception room', 'value': '82 degrees fahrenheit'}`.
For experimentation, we provide the validation dataset located in the `dev-A` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. It was created using the same pipeline as the `train` dataset.
For the sake of preliminary comparison of results between contestants and self-evaluation we provide test dataset located in `test-A` directory of `cnlps-caiccaic` repository.
It contains only input values, while expected values hidden for contestants and are used by gonito platform to evaluate submissions.
The test set prepared for the final evaluation will be released on May 17, 2023, and placed in the `test-B` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The goal of the task is to develop NLU models that are robust to speech recognition errors regardless of their type and origin, therefore participants **should not** assume that the same TTS and ASR models will be used for the preparation of the test data as for the preparation of the training data. Also, the ratio of utterances containing speech recognition errors to intact utterances will vary, with far more erroneous samples found in the test set.
| | Train | Test |
|------------|-------------|------------|
|Sentences | 14524 | 3633 |
|Avg length | 9.35 | 9.28 |
|Min length | 1 | 1 |
|Max length | 33 | 30 |
|Domains | 21 | 21 |
|Intents | 193 | 193 |
|Slots types | 80 | 79 |
## Submissions
- The solutions for the task are to be submitted via the Gonito platform challenge available at .
- For `in.tsv` file located in `test-A` (or `test-B`) directory, the participants are expected to provide `out.tsv` file in the same directory.
- Each row of `out.tsv` should contain the predictions for the corresponding row in `in.tsv`.
- The format of `out.tsv` file is the same as the format of `train/expected.tsv`.
## Rules
1. Participants are allowed to use any publicly available data.
2. Participants are allowed to use any publicly available pre-trained models.
3. Manual labeling is forbidden.
4. Max. 5 submissions per day are allowed.
5. Teams may consist of one or more people. There is no restriction on the size of the team. Only one team representative should submit the team's solution to the platform.
6. If it turns out that the solutions submitted by two different teams have the same score, the team that submitted the solution earlier would be ranked higher.
7. To be included in the final ranking, a team should provide a report describing their solution.
8. The report should conform to the requirements specified in the exemplary document provided at .
9. The best scoring submission on `test-B` for which a report is provided wins.
## Special session at FedCSIS 2023:
The authors of selected submissions will be invited to prepare the extended versions of their reports for publication in the conference proceedings and presentation at FedCSIS 2023. The Organizing Committee will make the selection based on the final evaluation results, the quality of submitted reports, and the originality of the presented methods.
## Evaluation
To create the final ranking, the submissions will be scored using **Exact Match Accuracy** (EMA), i.e.
> the percentage of utterance-level predictions in which domain, intent, and all the slots are correct.
Besides EMA scores, we will also report the following auxiliary metrics:
1. Domain accuracy:
> the percentage of utterances with correct domain prediction.
2. Intent accuracy:
> the percentage of utterances with the correct intent prediction.
3. Slot Word Recognition Rate:
> Word Recognition Rate calculated on slot annotations which is the percentage of correctly annotated slot values.
## Organizing Committee
- Marek Kubis, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poland
- Paweł Skórzewski, Adam Mickiewicz University, Poland
- Marcin Sowański, Samsung Research Poland
- Tomasz Ziętkiewicz, Samsung Research Poland
We set up a “CNLPS” Discord server to discuss the CAICCAIC challenge. Please join it to ask any task-related questions: https://discord.gg/VvjHhh7rbF
 ## Dates
- Feb 13, 2023: Training data available (English)
- Feb 20, 2023: Training data available (other languages)
- May 17, 2023: Test data available
- May 31, 2023: Deadline for submitting the results
- June 04, 2023: Announcement of the final results, sending invitations for submitting papers
- July 04, 2023: Deadline for submitting invited papers
- July 11, 2023: Author notification
- July 31, 2023: Final paper submission, registration
- Sept 20, 2023: Challenges in Natural Language Processing Symposium
## Data
The training set is derived from [Leyzer: A Dataset for Multilingual Assistants](https://github.com/cartesinus/leyzer). It consists of user utterances along with the semantic representation of the commands targeted at a virtual assistant. A fraction of the utterances in the training set is contaminated with speech recognition errors; however, to make the task more challenging, we left the majority of the utterances intact. The erroneous samples were obtained from user utterances using a TTS model followed by an ASR system.
## Dates
- Feb 13, 2023: Training data available (English)
- Feb 20, 2023: Training data available (other languages)
- May 17, 2023: Test data available
- May 31, 2023: Deadline for submitting the results
- June 04, 2023: Announcement of the final results, sending invitations for submitting papers
- July 04, 2023: Deadline for submitting invited papers
- July 11, 2023: Author notification
- July 31, 2023: Final paper submission, registration
- Sept 20, 2023: Challenges in Natural Language Processing Symposium
## Data
The training set is derived from [Leyzer: A Dataset for Multilingual Assistants](https://github.com/cartesinus/leyzer). It consists of user utterances along with the semantic representation of the commands targeted at a virtual assistant. A fraction of the utterances in the training set is contaminated with speech recognition errors; however, to make the task more challenging, we left the majority of the utterances intact. The erroneous samples were obtained from user utterances using a TTS model followed by an ASR system.
 The training data are located in the `train` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The `train` directory contains two files:
- **in.tsv** with four columns:
a. sample identifier: `306`,
b. language code: `en-US`,
c. data split type: `train`,
d. utterance: `adjust the temperature to 82 degrees fahrenheit on my reception room thermostat`.
- **expected.tsv** with three columns representing:
a. domain label: `Airconditioner`,
b. intent label: `SetTemperatureToValueOnDevice`,
c. annotations for slot values: `{'device_name': 'reception room', 'value': '82 degrees fahrenheit'}`.
For experimentation, we provide the validation dataset located in the `dev-A` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. It was created using the same pipeline as the `train` dataset.
For the sake of preliminary comparison of results between contestants and self-evaluation we provide test dataset located in `test-A` directory of `cnlps-caiccaic` repository.
It contains only input values, while expected values hidden for contestants and are used by gonito platform to evaluate submissions.
The test set prepared for the final evaluation will be released on May 17, 2023, and placed in the `test-B` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The goal of the task is to develop NLU models that are robust to speech recognition errors regardless of their type and origin, therefore participants **should not** assume that the same TTS and ASR models will be used for the preparation of the test data as for the preparation of the training data. Also, the ratio of utterances containing speech recognition errors to intact utterances will vary, with far more erroneous samples found in the test set.
| | Train | Test |
|------------|-------------|------------|
|Sentences | 14524 | 3633 |
|Avg length | 9.35 | 9.28 |
|Min length | 1 | 1 |
|Max length | 33 | 30 |
|Domains | 21 | 21 |
|Intents | 193 | 193 |
|Slots types | 80 | 79 |
## Submissions
- The solutions for the task are to be submitted via the Gonito platform challenge available at
The training data are located in the `train` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The `train` directory contains two files:
- **in.tsv** with four columns:
a. sample identifier: `306`,
b. language code: `en-US`,
c. data split type: `train`,
d. utterance: `adjust the temperature to 82 degrees fahrenheit on my reception room thermostat`.
- **expected.tsv** with three columns representing:
a. domain label: `Airconditioner`,
b. intent label: `SetTemperatureToValueOnDevice`,
c. annotations for slot values: `{'device_name': 'reception room', 'value': '82 degrees fahrenheit'}`.
For experimentation, we provide the validation dataset located in the `dev-A` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. It was created using the same pipeline as the `train` dataset.
For the sake of preliminary comparison of results between contestants and self-evaluation we provide test dataset located in `test-A` directory of `cnlps-caiccaic` repository.
It contains only input values, while expected values hidden for contestants and are used by gonito platform to evaluate submissions.
The test set prepared for the final evaluation will be released on May 17, 2023, and placed in the `test-B` directory of the `cnlps-caiccaic` repository. The goal of the task is to develop NLU models that are robust to speech recognition errors regardless of their type and origin, therefore participants **should not** assume that the same TTS and ASR models will be used for the preparation of the test data as for the preparation of the training data. Also, the ratio of utterances containing speech recognition errors to intact utterances will vary, with far more erroneous samples found in the test set.
| | Train | Test |
|------------|-------------|------------|
|Sentences | 14524 | 3633 |
|Avg length | 9.35 | 9.28 |
|Min length | 1 | 1 |
|Max length | 33 | 30 |
|Domains | 21 | 21 |
|Intents | 193 | 193 |
|Slots types | 80 | 79 |
## Submissions
- The solutions for the task are to be submitted via the Gonito platform challenge available at