478 KiB
Regresja wielomianowa
Celem regresji wielomianowej jest zamodelowanie relacji między zmienną zależną od zmiennych niezależnych jako funkcję wielomianu n-tego stopnia.
Postać ogólna regresji wielomianowej:
$$ h_{\theta}(x) = \sum_{i=0}^{n} \theta_i x^i $$
Gdzie:
$$ \theta - \text{wektor parametrów modelu} $$
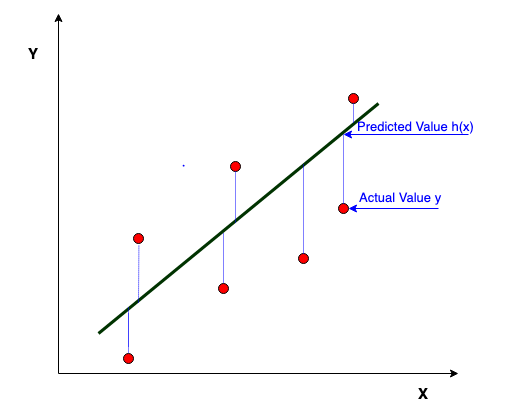
Funkcja kosztu
W celu odpowiedniego dobrania parametrów modelu, trzeba znaleźć minimum funkcji kosztu zdefiniowanej poniższym wzorem:
$$ J = \frac{1}{2m} (X \theta - y)^T (X \theta - y) $$
Gdzie:
$$ m - \text{ilość przykładów} $$
Za funkcję kosztu przyjmuje się zmodyfikowaną wersję błędu średniokwadratowego. Dodatkowo dodaje się dzielenie przez 2*m zamiast m, aby gradient z funkcji był lepszej postaci.
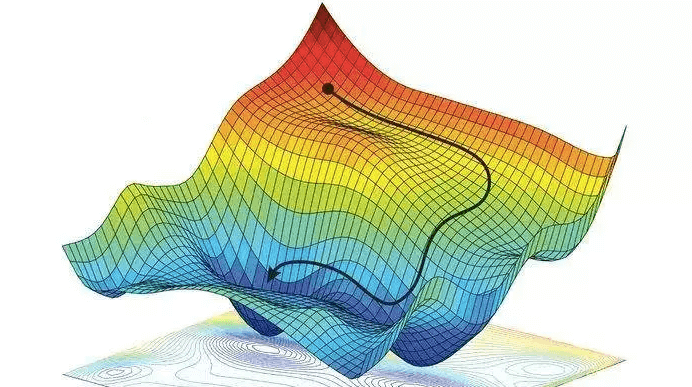
Do znalezienia minimum funckji kosztu można użyć metody gradientu prostego. W tym celu iteracyjnie liczy się gradient funkcji kosztu i aktualizuje się za jego pomocą wektor parametrów modelu aż do uzyskania zbieżności (Różnica między obliczoną funkcją kosztu a funkcją kosztu w poprzedniej iteracji będzie mniejsza od ustalonej wcześniej wartości $\varepsilon$).
Gradient funkcji kosztu:
$$ \dfrac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta} = \frac{1}{m}X^T(X \theta - y)$$
Modyfikacja parametrów modelu:
$$ \theta_{new} = \theta - \alpha * \dfrac{\partial J(\theta)}{\partial \theta}$$
Gdzie:
$$ \alpha - \text{współczynnik uczenia} $$
import ipywidgets as widgets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas
%matplotlib inline# Przydatne funkcje
cost_functions = dict()
def cost(theta, X, y):
"""Wersja macierzowa funkcji kosztu"""
m = len(y)
J = 1.0 / (2.0 * m) * ((X * theta - y).T * (X * theta - y))
return J.item()
def gradient(theta, X, y):
"""Wersja macierzowa gradientu funkcji kosztu"""
return 1.0 / len(y) * (X.T * (X * theta - y))
def gradient_descent(fJ, fdJ, theta, X, y, alpha=0.1, eps=10**-7):
"""Algorytm gradientu prostego"""
current_cost = fJ(theta, X, y)
logs = [[current_cost, theta]]
while True:
theta = theta - alpha * fdJ(theta, X, y)
current_cost, prev_cost = fJ(theta, X, y), current_cost
# print(current_cost)
if abs(prev_cost - current_cost) > 10**15:
print('Algorytm nie jest zbieżny!')
break
if abs(prev_cost - current_cost) <= eps:
break
logs.append([current_cost, theta])
return theta, logs
def plot_data(X, y, xlabel, ylabel):
"""Wykres danych"""
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16*.6, 9*.6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.1, right=0.9, bottom=0.1, top=0.9)
ax.scatter([X[:, 1]], [y], c='r', s=50, label='Dane')
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel)
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
ax.margins(.05, .05)
plt.ylim(y.min() - 1, y.max() + 1)
plt.xlim(np.min(X[:, 1]) - 1, np.max(X[:, 1]) + 1)
return fig
def plot_data_cost(X, y, xlabel, ylabel):
"""Wykres funkcji kosztu"""
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16 * .6, 9 * .6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.1, right=0.9, bottom=0.1, top=0.9)
ax.scatter([X], [y], c='r', s=50, label='Dane')
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel)
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
ax.margins(.05, .05)
plt.ylim(min(y) - 1, max(y) + 1)
plt.xlim(np.min(X) - 1, np.max(X) + 1)
return fig
def plot_fun(fig, fun, X):
"""Wykres funkcji `fun`"""
ax = fig.axes[0]
x0 = np.min(X[:, 1]) - 1.0
x1 = np.max(X[:, 1]) + 1.0
Arg = np.arange(x0, x1, 0.1)
Val = fun(Arg)
return ax.plot(Arg, Val, linewidth='2')def MSE(Y_true, Y_pred):
"""Błąd średniokwadratowy - Mean Squared Error"""
return np.square(np.subtract(Y_true,Y_pred)).mean()# Funkcja regresji wielomianowej
def h_poly(Theta, x):
"""Funkcja wielomianowa"""
return sum(theta * np.power(x, i) for i, theta in enumerate(Theta.tolist()))
def get_poly_data(data, deg):
"""Przygotowanie danych do regresji wielomianowej"""
m, n_plus_1 = data.shape
n = n_plus_1 - 1
X1 = data[:, 0:n]
X1 /= np.amax(X1, axis=0)
Xs = [np.ones((m, 1)), X1]
for i in range(2, deg+1):
Xn = np.power(X1, i)
Xn /= np.amax(Xn, axis=0)
Xs.append(Xn)
X = np.matrix(np.concatenate(Xs, axis=1)).reshape(m, deg * n + 1)
y = np.matrix(data[:, -1]).reshape(m, 1)
return X, y
def polynomial_regression(X, y, n):
"""Funkcja regresji wielomianowej"""
theta_start = np.matrix([0] * (n+1)).reshape(n+1, 1)
theta, logs = gradient_descent(cost, gradient, theta_start, X, y)
return lambda x: h_poly(theta, x), logsdef predict_values(model, data, n):
"""Funkcja predykcji"""
x, y = get_poly_data(np.array(data), n)
preprocessed_x = []
for i in x:
preprocessed_x.append(i.item(1))
return y, model(preprocessed_x), MSE(y, model(preprocessed_x))
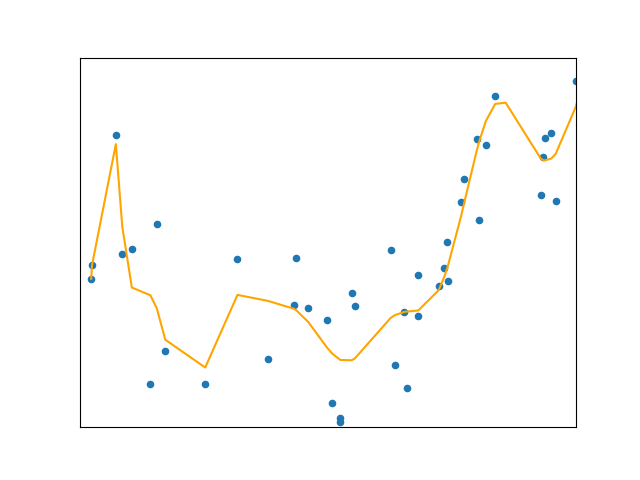
def plot_and_mse(data, data_test, n):
"""Wykres wraz z MSE"""
x, y = get_poly_data(np.array(data), n)
model, logs = polynomial_regression(x, y, n)
cost_function = [[element[0], i] for i, element in enumerate(logs)]
cost_functions[n] = cost_function
fig = plot_data(x, y, xlabel='x', ylabel='y')
plot_fun(fig, model, x)
y_true, Y_pred, mse = predict_values(model, data_test, n)
print(f'Wielomian {n} stopnia, MSE = {mse}')# Wczytanie danych (mieszkania) przy pomocy biblioteki pandas
alldata = pandas.read_csv('data_flats.tsv', header=0, sep='\t',
usecols=['price', 'rooms', 'sqrMetres'])
alldata = alldata[['sqrMetres', 'price']]
alldata = alldata.sample(frac=1)
alldata| sqrMetres | price | |
|---|---|---|
| 651 | 40 | 245832.0 |
| 1254 | 35 | 180000.0 |
| 1183 | 92 | 429000.0 |
| 1196 | 54 | 156085.0 |
| 1463 | 62 | 339282.0 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 994 | 33 | 207000.0 |
| 657 | 74 | 400000.0 |
| 1365 | 55 | 535000.0 |
| 934 | 72 | 430000.0 |
| 546 | 120 | 535000.0 |
1674 rows × 2 columns
# alldata = np.matrix(alldata[['sqrMetres', 'price']])
data_train = alldata[0:1600]
data_test = alldata[1600:]
data_train = np.matrix(data_train).astype(float)
data_test = np.matrix(data_test).astype(float)cost_fun_slices = []
for n in range(1, 4):
plot_and_mse(data_train, data_test, n)
cost_data = cost_functions.get(n)
cost_x = [line[1] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_y = [line[0] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_fun_slices.append((cost_x, cost_y))Wielomian 1 stopnia, MSE = 40830919432.83225 Wielomian 2 stopnia, MSE = 87109963962.58508 Wielomian 3 stopnia, MSE = 86319119164.94438
#WYKRESY FUNKCJI KOSZTU
for fig in cost_fun_slices:
cost_x, cost_y = fig
fig = plot_data_cost(cost_x, cost_y, "Iteration", "Cost function value")# Wczytanie danych przy pomocy biblioteki pandas
alldata_p2 = pandas.read_csv('polynomial-regression_2.csv')
alldata_p2 = alldata_p2.sample(frac=1)
alldata_p2| araba_fiyat | araba_max_hiz | |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 100 | 200 |
| 1 | 70 | 180 |
| 11 | 750 | 360 |
| 8 | 300 | 300 |
| 6 | 200 | 240 |
| 5 | 150 | 220 |
| 13 | 2000 | 365 |
| 7 | 250 | 240 |
| 9 | 400 | 350 |
| 0 | 60 | 180 |
| 12 | 1000 | 365 |
| 10 | 500 | 350 |
| 4 | 120 | 200 |
| 14 | 3000 | 365 |
| 2 | 80 | 200 |
# alldata = np.matrix(alldata[['sqrMetres', 'price']])
data_train_p2 = alldata_p2[0:12]
data_test_p2 = alldata_p2[12:]
data_train_p2 = np.matrix(data_train_p2).astype(float)
data_test_p2 = np.matrix(data_test_p2).astype(float)cost_fun_slices = []
for n in range(1, 4):
plot_and_mse(data_train_p2, data_test_p2, n)
cost_data = cost_functions.get(n)
cost_x = [line[1] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_y = [line[0] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_fun_slices.append((cost_x, cost_y))Wielomian 1 stopnia, MSE = 16499.91920339438 Wielomian 2 stopnia, MSE = 11862.306362249277 Wielomian 3 stopnia, MSE = 14326.050185115093
#WYKRESY FUNKCJI KOSZTU
for fig in cost_fun_slices:
cost_x, cost_y = fig
fig = plot_data_cost(cost_x, cost_y, "Iteration", "Cost function value")# Ilość nauki do ocenydata_marks_all = pandas.read_csv('Student_Marks.csv')
data_marks_all| number_courses | time_study | Marks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 4.508 | 19.202 |
| 1 | 4 | 0.096 | 7.734 |
| 2 | 4 | 3.133 | 13.811 |
| 3 | 6 | 7.909 | 53.018 |
| 4 | 8 | 7.811 | 55.299 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 95 | 6 | 3.561 | 19.128 |
| 96 | 3 | 0.301 | 5.609 |
| 97 | 4 | 7.163 | 41.444 |
| 98 | 7 | 0.309 | 12.027 |
| 99 | 3 | 6.335 | 32.357 |
100 rows × 3 columns
data_marks_all = data_marks_all[['time_study', 'Marks']]
# data_marks_all = data_marks_all.sample(frac=1)
data_marks_train = data_marks_all[0:70]
data_marks_test = data_marks_all[70:]
data_marks_train = np.matrix(data_marks_train).astype(float)
data_marks_test = np.matrix(data_marks_test).astype(float)cost_fun_slices = []
for n in range(1, 4):
plot_and_mse(data_marks_train, data_marks_test, n)
cost_data = cost_functions.get(n)
cost_x = [line[1] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_y = [line[0] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_fun_slices.append((cost_x, cost_y))Wielomian 1 stopnia, MSE = 381.16937283505433 Wielomian 2 stopnia, MSE = 394.1863119057109 Wielomian 3 stopnia, MSE = 391.5017110730558
#WYKRESY FUNKCJI KOSZTU
for fig in cost_fun_slices:
cost_x, cost_y = fig
fig = plot_data_cost(cost_x, cost_y, "Iteration", "Cost function value")data_ins = pandas.read_csv('insurance.csv')
data_ins = data_ins.sample(frac=1)
data_ins| age | sex | bmi | children | smoker | region | charges | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 949 | 25 | male | 29.700 | 3 | yes | southwest | 19933.45800 |
| 166 | 20 | female | 37.000 | 5 | no | southwest | 4830.63000 |
| 365 | 49 | female | 30.780 | 1 | no | northeast | 9778.34720 |
| 1183 | 48 | female | 27.360 | 1 | no | northeast | 9447.38240 |
| 772 | 44 | female | 36.480 | 0 | no | northeast | 12797.20962 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 1205 | 35 | male | 17.860 | 1 | no | northwest | 5116.50040 |
| 158 | 30 | male | 35.530 | 0 | yes | southeast | 36950.25670 |
| 740 | 45 | male | 24.035 | 2 | no | northeast | 8604.48365 |
| 907 | 44 | female | 32.340 | 1 | no | southeast | 7633.72060 |
| 1162 | 30 | male | 38.830 | 1 | no | southeast | 18963.17192 |
1338 rows × 7 columns
data_ins = data_ins[['age', 'charges']]
data_ins_train = data_ins[0:1200]
data_ins_test = data_ins[1200:]
data_ins_train = np.matrix(data_ins_train).astype(float)
data_ins_test = np.matrix(data_ins_test).astype(float)cost_fun_slices = []
for n in range(1, 4):
plot_and_mse(data_ins_train, data_ins_test, n)
cost_data = cost_functions.get(n)
cost_x = [line[1] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_y = [line[0] for line in cost_data[:250]]
cost_fun_slices.append((cost_x, cost_y))Wielomian 1 stopnia, MSE = 183212045.05222273 Wielomian 2 stopnia, MSE = 183706365.10358346 Wielomian 3 stopnia, MSE = 183691092.4723696
#WYKRESY FUNKCJI KOSZTU
for fig in cost_fun_slices:
cost_x, cost_y = fig
fig = plot_data_cost(cost_x, cost_y, "Iteration", "Cost function value")